
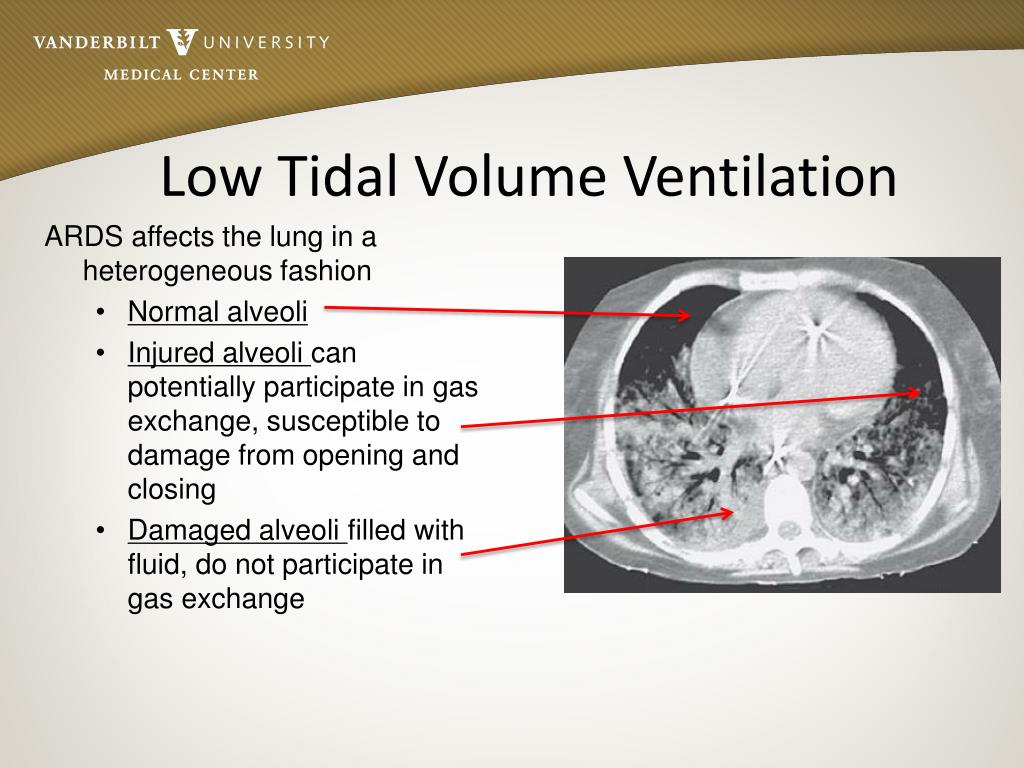
Conceivably, any further inflation to even higher volumes increases the risk of VILI development because of global overinflation. The potentially detrimental effects of ventilation at high absolute lung volumes can be quantified using the concept of stress and strain: when the lungs are inflated with elastance-based transpulmonary pressure (stress) of 27 mbar, they typically reach a strain of 2.0, corresponding to an inflation to twice their resting volume (functional residual capacity, FRC). Cyclic opening and closing of lung units may lead to atelectrauma, whereas ventilation at high lung volumes may lead to overdistension and barotrauma. The morphological features of ARDS, namely regional atelectasis, overdistension and presence of lung inhomogeneities pose patients at an increased risk of developing ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI). Mechanical ventilation is a life-saving treatment for critically ill patients suffering from acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
VENT TIDAL VOLUME CHART TRIAL
Trial registrationThis study was registered at (NCT02703012) on Mabefore including the first patient. ConclusionsĪdjustment of PEEP and V T using the EIT-based protocol led to individualization of ventilator settings with improved oxygenation and reduced alveolar cycling without promoting global overdistension. Compliance remained similar, while oxygenation was significantly improved and alveolar cycling was reduced after EIT-based optimization. Global lung stress remained below 27 mbar in all patients and global strain below 2.0 in 19 out of 20 patients. Prospective optimization of mechanical ventilation with EIT led to higher PEEP levels (16.5 mbar vs. To assess global overdistension, we determined whether lung stress and strain remained below 27 mbar and 2.0, respectively. Subsequently, ventilator settings were adjusted according to the EIT-based protocol once every 30 min for a duration of 4 h.
Initially, patients were ventilated according to the recommendations of the ARDS Network with a V T of 6 ml per kg predicted body weight and PEEP adjusted according to the lower PEEP/FiO 2 table. MethodsĢ0 patients with ARDS were included. The aim of this study was to assess whether the EIT-based protocol allows individualization of ventilator settings without causing lung overdistension, and to evaluate its effects on respiratory system compliance, oxygenation and alveolar cycling. We developed a protocol for individualization of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and tidal volume ( V T) utilizing EIT-derived information on recruitability, overdistension and alveolar cycling. In mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), electrical impedance tomography (EIT) provides information on alveolar cycling and overdistension as well as assessment of recruitability at the bedside.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
